Vehicle / Infrastructure ITS.

Introduction
Infrastructure based ITS systems require a communication link between the infrastructure and the vehicle. Early examples of such systems are toll roads- electronic road pricing- and vehicular access control systems.
Confusingly, many vehicle access control systems are not dealt with by any ITS or vehicle specific standardization committee, but fall within generic standards for RFID (Radio Frequency Identification). And these communications Standards are generally found within the purview of ISO/IEC JTC1 SC31 WG4 (Information Technology, Automatic Identification, Radio Frequency Identification).
Within this book Standards for such systems are identified in Chapter 7.4.
General aspects concerning Automatic Vehicle Identification and Automatic (transport related) Equipment Identification, and issues of Electronic Registration Identification are identified in Chapter 7.3.
Standards concerned with Electronic Tolling (often known as ETC, AFC, ATC etc) are developed by ISO TC204 WG5/CEN TC278 WG1. such systems are identified in Chapter 8.8.
It is worth noting that while in Europe, with the exception of Italy, there is a coalescence around the ETSI /CEN standards for EFC, and these standards are widely used in Australia and parts of Asia, in North America there are no properly developed EFC/ETC Standards and in consequence the market in those countries has become dominated by three commercially proprietary systems. China currently uses several different systems and is developing its own National Standard and Japan and Korea have National standards.
For early generation systems, standards were developed as complete whole closed systems, including the communications aspects- the air interface protocols. Later work has separated the applications from the carrier communications, and it is envisioned that, in the future, such fee collection transactions, whether for simple toll collection or more complex road pricing and demand management systems, will be transacted using a generic vehicle communications system, perhaps linked to a smart card or other device within the vehicle.
In order to perform many ITS services, as currently envisioned, expects that vehicles will be equipped with one or more communication systems that use one or more wireless air interfaces to interact between the vehicle and service provision via the infrastructure
Examples (but not a complete list) of Vehicle– Infrastructure services, where WIP is known to be underway are as follows, however it should be noted that there is no absolute consensus as to the extent of many of the services, nor of the means of achieving them. For this reason, the descriptions are generalised and not specific, and services might exist in multiple categories :
Infrastructure <-> Vehicle Safety Services
Infrastructure To On-Board Equipment

Accident Site Advisory
After a crash is reported, either electronically by an emergency call message transmission, or by a first responder or PSAP, a warning is transmitted from the nearest infrastructure beacon, or from a portable beacon carried by emergency services, or if it is capable post crash from one or more of the affected vehicles, to all other vehicles in the area warning of the proximity of the accident. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.
Animal Crossing Zone Information
Provision of warnings to drivers at farm crossings, horse trail crossings/bridleways etc. The information is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.
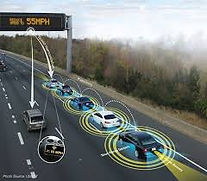
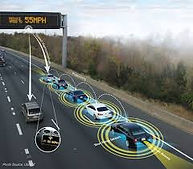
Adaptive Drivetrain Management-Infrastructure Assisted
See also In-vehicle systems in Adaptive Drivetrain Management.
By anticipating certain driving situations an on-board system can recommend handling strategies to the driver and fuel consumption improvement can be derived, and safety and performance improvements achieved. By interacting with the infrastructure, information about upcoming driving conditions, collated by sensor or probe vehicles and reported to the infrastructure, can be introduced to the calculation models to further improve the efficiency of such systems. The information is carried into the vehicle via an ITS communications interface.

Adaptive Headlight Aiming
Provision of information to vehicles to change headlamp settings to local conditions.) See also in-vehicle systems Adaptive Headlamp Aiming
Early instantiations are in-vehicle devices controlled solely by in-vehicle sensors and are already in the market place. Devices under development interact with the infrastructure and/or other vehicles and in these devices the information is carried into the vehicle via an ITS communications interface.

Blind Merge Warning
Provision of warnings (from the infrastructure) to drivers where highways or lanes merge. These in-vehicle electronic systems monitor the position of a vehicle within a roadway lane and warn a driver if it is unsafe to change lanes or merge into a line of traffic. These systems are rearward-looking, radar-based systems. They assist drivers who are intentionally changing lanes by detecting vehicles in the driver's blind spot. The warning is carried into the vehicle via an ITS communications interface.

Curve Speed Warning- Infrastructure based
Provision of warnings from the infrastructure to drivers to adapt speed to curve (bend) conditions. May be adaptive to weather and road conditions at the time. Curve speed warning systems use roadside detectors and electronic warning signs to warn drivers, typically those in commercial trucks and other heavy vehicles, of potentially dangerous speeds in approach to curves on highways. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Emergency Vehicle Signal Preemption
The control of traffic signals to give priority to emergency vehicles (obviating the need for emergency vehicles to cross signals set at stop). Emergency Vehicle preemption allows fire trucks and ambulances to intervene in the normal operation of traffic control systems using wireless communications installed on traffic intersections and emergency vehicles. As the emergency vehicle approaches a traffic signal, it is recognized by the traffic signal controller through light, radio waves, or sound. The normal green-yellow-and-red cycle can then be interrupted to change the light to green.

Emergency Vehicle Warning – From Infrastructure
Infrastructure based systems, having knowledge of the site of and incident, and notified by an emergency response vehicle towards the incident, either broadcast, or notify vehicles registered by the beacon as being within its range, of the approach of an emergency vehicle. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

External Speed Limitation
The limitation of speed either to local road regulations or at high risk points such as the proximity to schools, parks etc. The limitation is achieved by the receipt of an appropriate message over an air interface which instructs the engine management system to control speed to a maximum of that required in the transmitted message.

Fog Warning
Provision of warnings from the infrastructure to drivers of the presence of fog at or ahead of the vehicle. Such systems may be provided from a central reference to the location of the vehicle and known ground conditions at that point or ahead of that point, or may comprise a self-contained ITS broadcast transmitter, or vehicle presence sensing transmitter installed throughout the road and/or in known fog zone areas where during foggy conditions motorists are alerted of the fog zone condition ahead. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications

Freezing/Icy Bridge Warning
Provision of warnings from the infrastructure to drivers of the presence of ice on a bridge ahead.
Such systems may be provided from a central reference to the location of the vehicle matched to information collected from sensors in the bridge, or may comprise a self-contained ITS broadcast transmitter, or vehicle presence sensing transmitter, connected to sensors in the bridge, and attached to (or in place of) an appropriately placed warning sign. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Freezing/Icy Road Surface Warning
Provision of warnings from the infrastructure to drivers of the presence of icy on the road.
Such systems may be provided from a central reference to the location of the vehicle matched to information collected from sensors in the road, or may comprise a self-contained ITS broadcast transmitter, or vehicle presence sensing transmitter, connected to sensors in the road, and attached to (or in place of) an appropriately placed warning sign. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Hazardous Warnings Restricted Area
There are multiple approaches to such situations.
a) Provision of warnings from the infrastructure to drivers of HAZMAT vehicles when approaching restricted areas. Such systems may be provided from a central reference to the location of the vehicle matched to known HAZMAT restricted zones, or may comprise a self-contained ITS broadcast transmitter, or vehicle presence sensing transmitter, installed on a HAZMAT restriction sign (or in lieu of) to provide warning to the driver. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.
b) HAZMAT vehicles may intermittently, continuously, or on command, transmit (with or without driver consent) nature of HAZMAT cargo, driver authentication and identification, etc. On receipt of a signal approaching or in a HAZMAT restricted area for that type of material, the driver is warned by audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface, or possibly the vehicle is immobilised and emergency/police summoned.

Highway/Rail Collision Warning.
The provision of warnings to both road and rail of potential collisions at grade (level) crossings; The control of road/rail vehicles to prevent collisions at grade (level) crossings. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Homeland Security Identification and Management
A range of vehicle and potentially occupant identification measures to support national security and border crossing identification and management.

Intelligent On-Ramp Metering
The development of ramp metering and monitoring systems to adapt more precisely to actual traffic flows; bringing ramp signals onboard to video/audio presentation; potential extension to prevent vehicles entering the highway when the signal is at stop.

Intelligent Traffic Lights
Collection of traffic information from vehicles to enable more intelligent operation of traffic lights to adapt to traffic flows, average speeds, incidents etc.
In such systems, all cars communicate to the traffic light using an ITS communications interface, both their specific place in the queue and their destination address. The traffic light control system has to decide which option (i.e. which lanes are to be put on green) is optimal to minimize the long-term average waiting time until all cars have arrived at their destination address. The traffic light controllers solve this problem by estimating how long it would take for a car to arrive at its destination address (for which the car may need to pass many different traffic lights) when currently the light would be put on green, and how long it would take if the light would be put on red. The difference between the waiting time for red and the waiting time for green is the gain for the car. The traffic light controllers set the lights in such a way to maximize the average gain of all cars standing before the crossing. Waiting times of individual cars are used to compute the long term average waiting times using dynamic programming algorithms.

Intersection Collision : Infrastructure-Based Warning
The provision of warnings initiated by the infrastructure to vehicles approaching or at intersections of potential collisions (especially at blind intersections).
Infrastructure-based intersection collision avoidance systems use roadside sensors, processors, and warning devices; roadside-vehicle communication devices; other roadside informational or warning devices; and traffic signals to provide driving assistance to motorists. The intersection collision avoidance systems can be classified as either infrastructure-only or as infrastructure vehicle cooperative. Infrastructure-only systems rely
solely on roadside warning devices to communicate with drivers. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Keep Clear Warning
Provision of warnings to drivers to avoid specific locations; may be because of obstacles in the road, damage to the road; congestion, road works, flood, high winds, accident, spillage etc. or because of local regulations. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Left Turn Assistant - Infrastructure Assisted
Provision of assistance to drivers turning left . This countermeasure involves warning motorists making a left turn at a traffic signal of a potential conflict with vehicles approaching from the opposite direction. (Causes a total of 192,000 crashes per year in USA {Barr, 2001}). The basic sensing requirements are to identify potential conflicts by determining the speed and the acceleration or deceleration rate of each vehicle approaching the intersection from the opposite direction, including vehicles executing through and right turn movements. Simple point measurements will not be sufficient, since vehicles can assume various trajectories and acceleration/deceleration/stopping movements, particularly when other vehicles are present. The assistance is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Low Bridge Warning
Provision of warnings to drivers at low bridges; probably matched to vehicle characteristics. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.
Low Parking Structure Warning
Provision of warnings to drivers of height restrictions in vehicle parks; probably matched to vehicle characteristics. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Merge Assistant
Provision of assistance to drivers merging into traffic lanes. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.
On-Board VMS signage
The provision to on-board video screens of messages transmitted to external Variable message signs, or the replacement of such signage by location related traffic information to vehicles from infrastructure communication points. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Pedestrian Crossing Information
The provision of information to drivers approaching pedestrian crossings; the provision of information to pedestrians at crossings (especially visually, aurally and mobility impaired pedestrians). The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.
Pedestrian Crossing Control
Vehicle control to prevent vehicles crossing pedestrian crossings while set to pedestrian priority /stop traffic or alternatively while physically in use by pedestrians. Control is effected via an ITS communications interface.
Pedestrian/Children Warning
Provision of warnings to drivers at points where pedestrians and particularly children are likely to appear in the road space (e.g. near schools etc.). The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Post-Crash Warning
Provision of warnings to drivers approaching the site of recent accidents. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Rail Road Crossing Warning
Provision of warnings from the infrastructure to drivers of rail crossings (grade crossings/ level crossings) ahead. Such systems may be provided from a central reference to the location of the vehicle matched to known crossings, or may comprise a self-contained ITS broadcast transmitter, or vehicle presence sensing transmitter, installed on a rail crossing warning sign (or in lieu of) to provide warning of the crossing ahead. Systems may also detect the presence of approaching trains to raise the warning level, and may provide date to trains where it appears the car is either stationary on the crossing, or likely to ignore the warnings. Later systems may force vehicles to stop when trains are approaching The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface. In the latter case, would directly link to vehicle control systems

Rest Area Ahead Advisory
A self self-contained intelligent beacon may be installed on a sign or the surface or side of the road to provide an in-vehicle reminder of the facilities provided at the rest area ahead. Such information may also be broadcast from an infrastructure beacon, transmitted once a vehicle is registered, and may be linked with the provision of commercial publicity information where the rest area offers commercial services. The notice is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Right Turn Assistant- Infrastructure Assisted
Provision of assistance to drivers turning right. See Left Turn Assistant. The assistance data is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Road Condition Warning- Infrastructure Assisted
Provision of warnings to drivers where there are adverse road conditions (for example : Ice, flood, obstacle in road, pothole, spillage, surface deformation etc). The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.
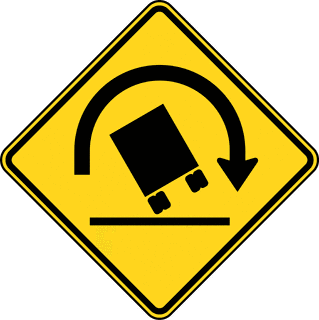
Rollover Warning
Provision of warnings to drivers of risk of vehicle rollover (due to adverse camber, crosswinds etc.) Rollover warning systems notify drivers when they are travelling too fast for an approaching curve, given their vehicles operating characteristics. Primarily targeted to heavy goods and high sided vehicles. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

School Bus Warning
An ITS communications device on-board the bus alerts approaching drivers (in both directions) of the impending danger surrounding the vehicles. Transmission signals may be intelligently programmed and transmitted in the forward (parallel) and/or reverse direction of the bus, or surrounding (up to 360 degree radius) the bus as needed to alert approaching vehicles in the vicinity of the potential danger.

School Zone Warning
Provision of warnings to drivers in the proximity of school entrances. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Sign information (warning assistance)
Transmission of road signs to in-vehicle video/audio display. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

SOS Services – Infrastructure assisted
Provision of connections to vehicles from police and emergency services for the transmission of voice and/or data communications. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Speed Limit Advisory
Provision of warnings from the infrastructure to drivers of local speed limits and warning when exceeding speed limits. Such systems may be provided from a central reference to the location of the vehicle matched to known speed limits, or may comprise a self-contained ITS broadcast transmitter, or vehicle presence sensing transmitter, installed on a speed limit sign (or in lieu of) to provide regulatory or recommended speed limit (in-vehicle signing) based on weather conditions, ice, rain, potential hazards, etc. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.
Speed Limit Control
Control of vehicle speed to prevent the vehicle exceeding the local speed limit. The control instruction is effected via an ITS communications interface.

Stop Sign Movement Assistance - Infrastructure Assisted
This countermeasure involves warning motorists discharging from a stop sign that their movement may conflict with another vehicle. The subject vehicle movement could be left turn, right turn, or through. (causing a total of 362,000 crashes per year in USA {Barr, 2001}.)
The basic sensing requirements are to identify potential conflicts by determining the speed, acceleration, or deceleration rate of each vehicle approaching the intersection and the discharge from the stop line for vehicles at stop-controlled approaches. The data and warnings are carried into the vehicle via an ITS communications interface and warnings displayed using audio /or visual display.

Stop Sign Warning
Provision of in-vehicle video screen and or audio sign warnings to drivers approaching stop signs; provision of roadside equipment that detects approaching vehicles and illuminates or otherwise highlight roadside signs to warn of stop sign being approached. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Traffic Signal Warning
Provision of warnings to drivers approaching traffic signal.
At its simplest, an ITS communications link associated with of the traffic signal, advises vehicles approaching in any particular direction of its status, and probably the time to change of status. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.
In more advanced systems, sensors may identify that the speed of an approaching vehicle to the intersection is outside the normal range, and ITS communications link associated with the traffic signal sends a distinct warning signal to the potentially violating vehicle and activates red light enforcement cameras.
Traffic Signal Violation Warning
This countermeasure involves (1) warning potential violators of a traffic signal to recognize the control device and (2) warning motorists on adjacent approaches of the potential conflict. The target crashes reflect causal factors of “did not see”, “ tried to beat the light”, or “deliberate violation”, (causing 288,000 crashes per year in USA {Barr, 2001}).
The basic sensing requirements are to identify potential (very highly likely) violators by determining the speed and possibly also the deceleration rate of each vehicle at a fixed location. The processing system will identify vehicles at an upstream control point that are unlikely to stop at the intersection. Preliminary calculations suggest, for example, that a vehicle travelling 30 mph at a point upstream from the line will very likely be incapable of stopping in time (at least without a severe braking event), and hence can be identified as a potential violator.
Once a violator is identified, warnings will be conveyed to the violator and also to other drivers on adjacent approaches to the intersection. The violator could be warned by: (1) Warning signs and lights activated once the potential violation is detected. For example, “Stop Ahead” warning signs could be used with a flashing amber light to draw attention to the signs, and located on both sides of the roadway to increase the likelihood that the subject driver would readily receive the warning. (2) A warning light could be incorporated directly in the traffic signal display itself, again to draw attention to the traffic control device. For example, strobe lights have been used to heighten the conspicuity of traffic signal displays for rural intersections where motorists may not expect a signal. (3) An intelligent rumble strip could be activated to warn the violator to slow down, and possibly heighten awareness of the need to stop at the intersection. (4) Variable message signs (VMS) could convey the warning to the driver.
Motorists on adjacent approaches also need to be warned of the potential violation and conflict, and could be warned by: (1) Warning lights activated to indicate a need for caution and possibly to indicate the source of the conflict. (2) An intelligent rumble strip activated to warn the other motorists to slow down and proceed cautiously at the intersection. (3) A VMS or graphic display sign used to warn drivers of the potential conflict with the signal violator, (but these might only be effective only where there is sufficient time for the motorists to comprehend the message and respond). The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.

Transit Vehicle Data Transfer- Safety
Transit (Public Transport) vehicles are increasingly monitored for both safety and commercial reasons. In respect of safety, transit vehicles are commonly monitored using on-board video camera’s and the ITS link can be used to manage and transfer video data and automatically raise alerts where problems occur. Transit vehicle priority at crossings can also be expedited using ITS technologies. Vehicle performance and maintenance issues can also obviate vehicle breakdowns, (which can be the cause of accidents either directly related to the breakdown, or passengers milling around in the road space following a breakdown.

Work Zone Warning
Provision of information to drivers of approaching roadwork zones, identification of upcoming changes to lanes available, speed limits and other restrictions. Multiple self-contained intelligent beacons may be installed in critical areas as deemed appropriate to provide for continued warnings of workers present in the immediate work zones. The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.
In the future, in-vehicle alerts may include self-controlled speed limitation of vehicle and autonomous deceleration in such areas.

Wrong-way Driver Warning- Infrastructure Assisted
Warnings to the road operator, road user and other road users of vehicles travelling in the wrong direction on a controlled direction carriageway.
Typically, a digital “smart camera” constantly observes the motorway exit. The movements of the vehicles driving past are analysed from the images. If a vehicle drives opposite the permitted direction, the “smart camera” triggers an alarm message to the traffic management and information centre, to the violating vehicle itself (where equipped with ITS communications) and to other traffic participants and response personnel.
The warning is carried into the vehicle audio and/or visual display via an ITS communications interface.



