Services to Public Transport Users and Pedestrians

Dynamic Ridesharing
A Ride Matching and Reservation user service provides real-time ride matching information and reservations to travellers in their homes, offices or other locations, and assists transportation providers with vehicle assignments and scheduling. The user service provides one of the basic tools for altering the travel behaviour of individuals who drive alone during congested periods.
For public transit, Route deviation schemes, where vehicles would leave a fixed route for a short distance to pick up or discharge passengers, is another approach employed to improve service. Vehicles providing this service can include small buses, taxicabs, or other small, shared-ride vehicles.


eCall for Pedestrians and Vulnerable Road Users
This sevice brings the benefits of eCall to pedestrians and vulnerable Road users via a smartphone or equipment embedded in wheelchairs/disability transporters

Emergency Call/Mayday Alert For Public Transport
Mayday requests from travellers, drivers, and transit vehicle operators are passed to the emergency system operator using an ITS or other communications link. The process receives acknowledgment of the emergency request from the system operator and passes the acknowledgment on to the requestor. This process inputs processing parameters for biometric image matching analysis from the system operator, and output those parameters to another process. That process in turn provides image matching results to this process, which are then returned to the system operator.
Intrusion Detection
Intrusion detection (or motion detection) at transit facilities (i.e., transit yards and shops). This process remotely monitors sensor data collected in secure areas, including those frequented by travellers (transit stops, rest areas, park and ride lots, modal interchange facilities, on-board transit vehicles, etc.), and those typically away from travellers (tunnels, bridges, roadway infrastructure, etc.). Sensor data can also be collected from other emergency centres and the process returns collected sensor data (raw and processed) to those centres. The types of sensor data include threat sensors (such as chemical, biological, explosives, and radiological), object detection sensors (such as metal detectors), motion and intrusion sensors, and infrastructure integrity sensors. In addition to raw sensor inputs, this process also receives data pre-processed in the field, and provides additional processing if directed by processing parameters established by centre personnel. The process can input threat information from field analysis functions and together with its own processing, identify potential threats, and verify those threats by correlating collected data. The process outputs identified threats to other processes for output to centre personnel and to support further threat analysis.

Paratransit Fleet Dispatch
Paratransit is an alternative mode of flexible passenger transportation that does not follow fixed routes or schedules. Typically vans or mini-buses are used to provide Paratransit service, but also share taxis (and in pats of Asia “jitneys” and “Tuk-Tuks”) are important providers. Paratransit services may vary considerably on the degree of flexibility they provide their customers. At their simplest they may consist of a taxi or small bus that will run along a more or less defined route and then stop to pick up or discharge passengers on request. At the other end of the spectrum -- fully Demand-Responsive Transport -- the most flexible Paratransit systems offer on-demand call-up door-to-door service from any origin to any destination in a service area. Paratransit services are normally operated by public transit agencies, community groups or not-for-profit corporations, and for-profit private companies or operators.
Such systems are optimised by sophisticated central planning and management. Typically with users calling in by phone or cellphone and the central control locating the best unit to respond. This is more complicated than simple shared ride taxis, because the destinations will differ more significantly, and so efficiency is gained by simultaneous multi destination routing.

Public Transport Fares Management
The management of Fare Collection by fare (basis of charge) category and payment type. As well as the use of ITS/IT/ICT to efficiently manage traffic flows and collect fares, this includes management of fare rates according to demand levels across the day, or on particular days, or long term price management to encourage/discourage usage patterns.

Public Transport /Transit Service Dispatch
Provides potential solutions to dispatchers and operators to optimise service dispatch and to to facilitate quick response to service delays and forecast service delays.
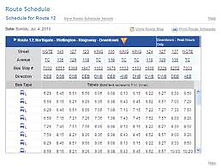
Public Transport Scheduling Services
Maintain transportation schedules and assure transfer connections from vehicle to vehicle and between modes, and can be coupled with traffic control services to facilitate quick response to service

Public Transport Service Planning
Public Transportation Service Planning automates the operations, planning and subsequently the management functions of public transit systems. It provides real-time computer analysis of vehicles and facilities to improve transit operations and maintenance This service help to maintain transportation schedules and assure transfer connections from vehicle to vehicle and between modes Service schedulers will have timely data to adjust trips. Personnel management can be enhanced with the automatic recording and verification of operating and maintenance task performance.
Public Transport Surveillance
Systems that monitor the environment in transit facilities, transit stations, parking lots, bus stops and on-board transit vehicles and generate alarms (either automatically or manually) when necessary. The service also provides systems that monitor key infrastructure of transit (rail track, bridges, tunnels, bus guideways, etc.).


Public Transport Vehicle Fleet Tracking
Monitors the location of transit vehicles, identifies deviations from the schedule, and offers potential solutions to dispatchers and operators. This service helps to maintain transportation schedules and assure transfer connections from vehicle to vehicle and between modes and can be coupled with traffic control services to facilitate quick response to service delays

Public Transport Vehicle Internal Systems Monitoring
For example measurement and reporting of tyre-pressures, the identity of towed trailers, suspension raising/lowering for improved access, engine efficiency and temperature, shock and vibration sensing, use of signal prioritisation.

Safety Enhancements For Vulnerable Road Users
This service group covers the application of ITS functionality to the enhancement of safety levels for vulnerable road user groups (particularly elderly or disabled and road maintenance workers). These groups include:
a) Motor cyclists
b) Pedal cyclists
c) Pedestrians
d) Smart pedestrian crossings (e.g. automatic warning of pedestrians for drivers, prolonging crossing times for elderly users, and changing pedestrian prioritisation).
e) Smart pedestrian crossings (e.g. prolonging crossing times for elderly and disabled users).
f) Vehicle presence detection(either to the vehicle or from the vehicle to the pedestrian)
g) Automatic advice to drivers by disabled road users (e.g. presence of wheel chair)
h) Intersection monitoring of specialized conveyances (e.g. wheelchairs, carts)
i) Driver warnings for specialized conveyances
j) Clarification of right of way rules
k) Onboard echo of warning signs
l) Identify by aural or tactile means the presence of oncoming vehicles
m) Warning of imminent signal phase change
n) Signal display advance warning
o) Oncoming vehicle advance warning (for non-signalised junction)
p) In-vehicle signage and warning systems

Silent Alarm
The provision of silent alarms via an ITS air interface or other means, including the provision of location information. silent activation of video cameras and the transmission of images. includes systems on-board the public transit vehicle (bus, rail car) for video, audio (including covert microphones that can be triggered by the transit vehicle operator), and event recorder (i.e., "black box") outputs to monitor activities, incidents, and potential threats. These systems and sensors are normally monitored by central dispatch.

Travel Services Information – Dedicated Location
Provides Travel Services Information specific to a location (for example, train station, football ground etc.)
Travel Services Information – Personal Interactive
The Traveller Services Information user service provides a business directory, or “yellow pages,” of information on travel-related services and facilities, for example the location, operating hours, and availability of food, lodging, parking, auto repair, hospitals, and police facilities. Traveller services information would be accessible in the home, office or other public locations to help plan trips, and it would also be available en-route. The service includes not only the traveller services information, but the capability to make reservations for many of the traveller services.
Personalized Public Transit user service supports flexibly routed transit vehicles. Small, publicly or privately operated vehicles provide on-demand routing to pick up passengers who have requested service and deliver them to their destinations



